In the modern world, being able to provide effective data security measures is essential for any organization in payment processing. The most effective method for keeping cardholder data safe is a multi-pronged approach, combining EMV, encryption and tokenization. This guide will focus on tokenization, understanding that it is only one part of an effective data security approach.
Tokenization substitutes a non-valuable "token" in place of sensitive cardholder data. This enhances data security by protecting the original data and limiting its exposure. For independent software vendors (ISVs) and their merchants, credit card tokenization is an important component of maintaining customers' security as they pay for products and services. This blog explains the tokenization process in-depth and shares some of the common applications of this technology.
How Does Credit Card Tokenization Work?
This step-by-step guide to credit card tokenization provides a thorough understanding of what happens during the tokenization process.
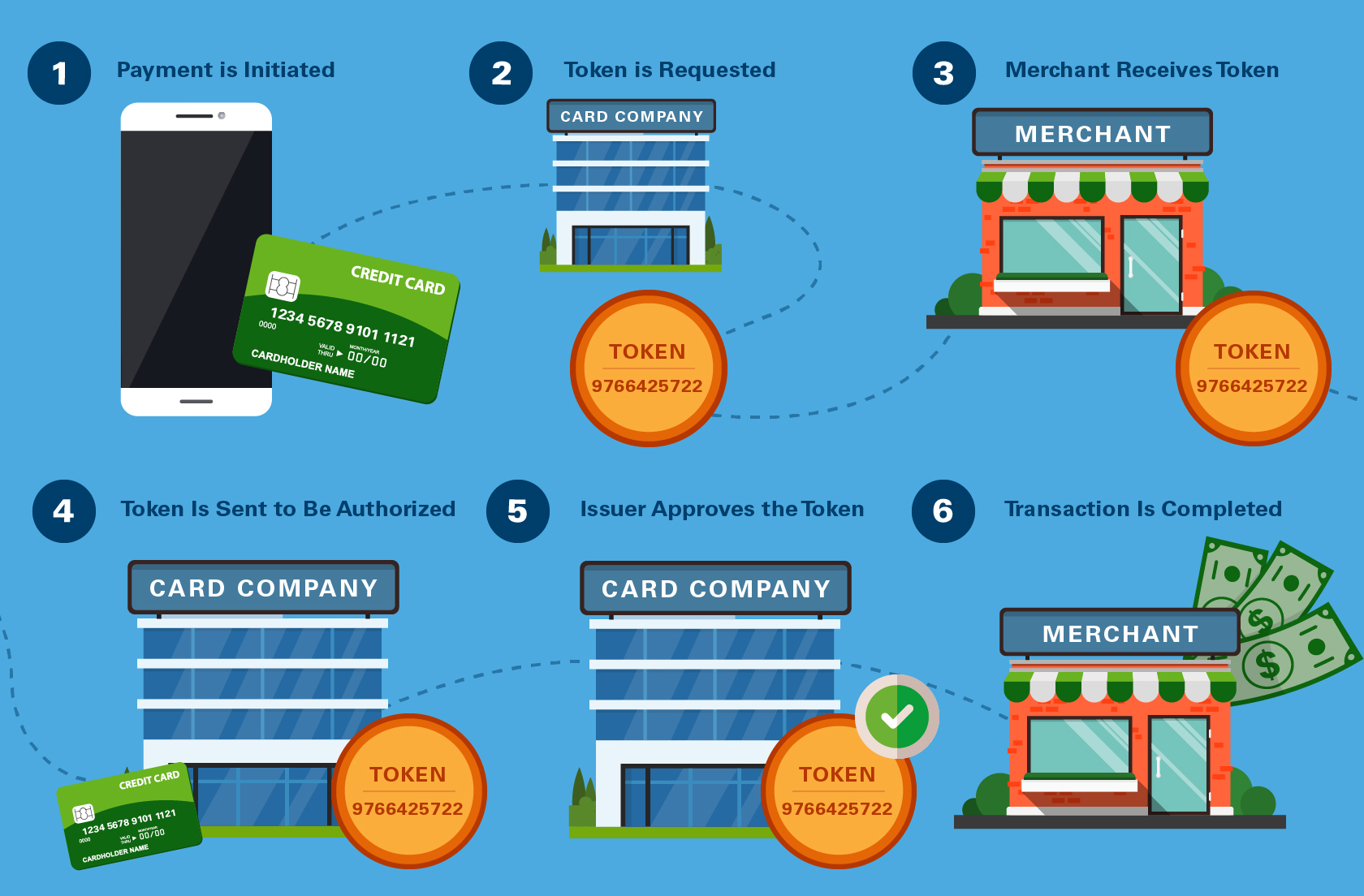
Step 1. Payment is initiated.
The process starts when the client initiates a payment by entering their credit card number with the company providing the transaction service. This may be for a single payment, or the customer may save their card for later purchases.
Step 2. Token is requested.
The credit card information can be replaced with a token as part of a payment or in a separate tokenization process. The company that receives the credit card information uses a service to turn the credit card number into a token. They may do this through the use of a remote token service server, or they may request a token from another provider. Often, the card company or bank behind the card itself will provide the token.
Step 3. Merchant receives token.
Once the token is handed to the requester, it’s essentially treated like the actual credit card number during the first part of the transaction. The shopkeeper will receive the token and pass it to the merchant acquirer to process the transaction.
Step 4. Token is sent to be authorized.
The issuer of the token, which may be a card company or other token service server, will take the token from the acquirer and compare it to their information to see if it is valid. They will have the option of either accepting or declining the transaction.
Step 5. Issuer approves the token.
If everything is approved, the issuer will send an authorization and payment back to the acquirer. This confirms that the token can be used to complete the transaction. During all of this, the merchant themselves will not see the card number. Instead, they will simply view the token and the authorization.
Step 6. Transaction is completed.
Once everything is approved, the transaction is completed. Money is transferred from the credit card company or client's account and sent to the merchant. In return, the customer will receive the goods or services they requested.
How Tokenization Is Used
The applications of credit card tokenization can be used in any type of environment where your merchant is accepting payments.
Credit card tokenization can be utilized in three main environments.



- Online - Tokenization can be used for a card not present transaction such as an online purchase
- In-Store - Tokenization can be used for card present transactions such as purchasing goods or services at a merchant’s store
- In-App/Mobile - Tokenization can be used for in-app purchases or mobile payments
Credit Card Tokenization and PCI Compliance
Any company that accepts credit cards must meet the requirements of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). One of the major principles of PCI DSS is protecting cardholder data, which is where tokenization comes in.
Those who want to achieve PCI compliance while offering card on file or recurring billing services can utilize tokens to eliminate storing cardholder data in their environment. This method of PCI data storage can drastically reduce risks since card numbers aren’t available anywhere besides the data vault and the original point of capture.
Conclusion
Tokenization is an essential aspect of data security.
ISVs that want to remain competitive and offer their customers the best possible service can greatly benefit from partnering with a company that includes tokenization in their security solutions.
At Global Payments Integrated, our EdgeShield Security Bundle provides advanced security services intended to protect credit card data, prevent counterfeit fraud, and enhance payments security. Through a unique collection of complementary security solutions, EdgeShield delivers one of the industry’s most secure payments platforms, combining EMV, encryption, and tokenization. When integrated into systems that accept payments, the bundle protects credit card data while at rest and in transit. To learn more about our security solutions, contact us today.
